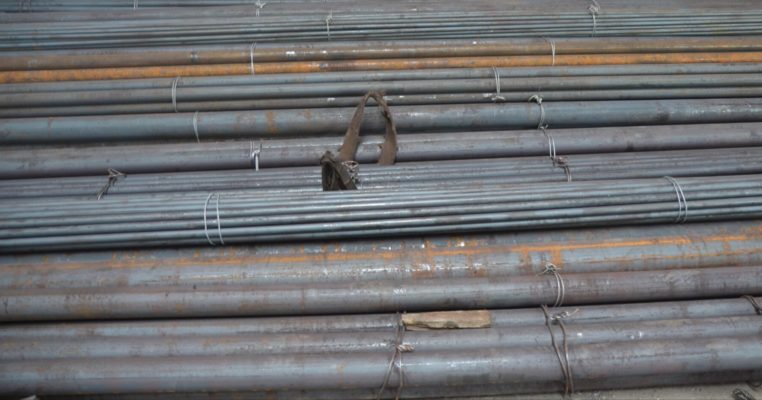
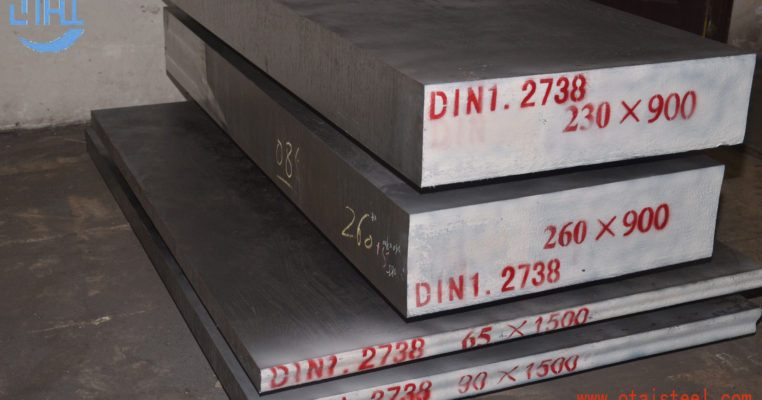
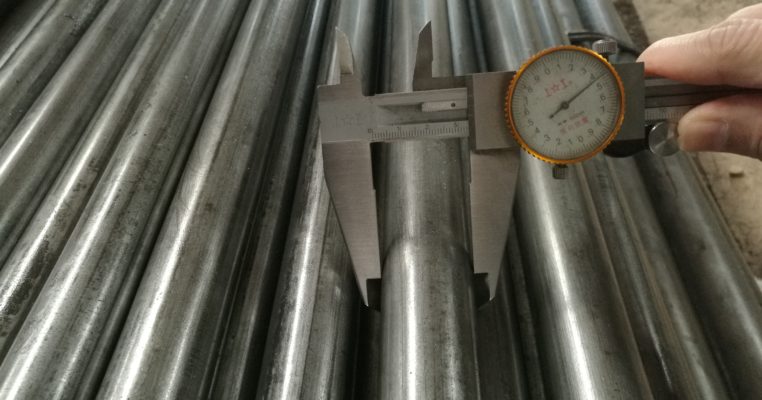
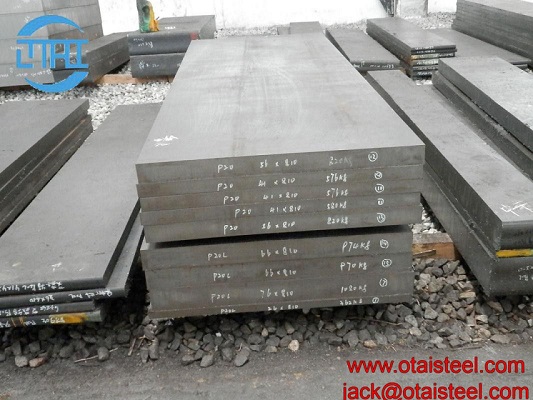
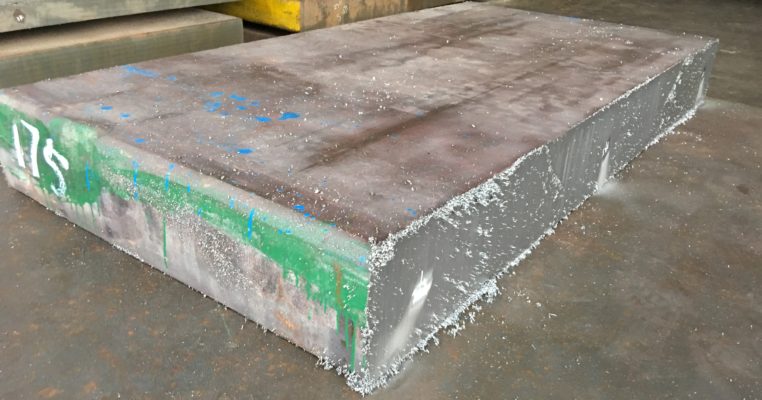
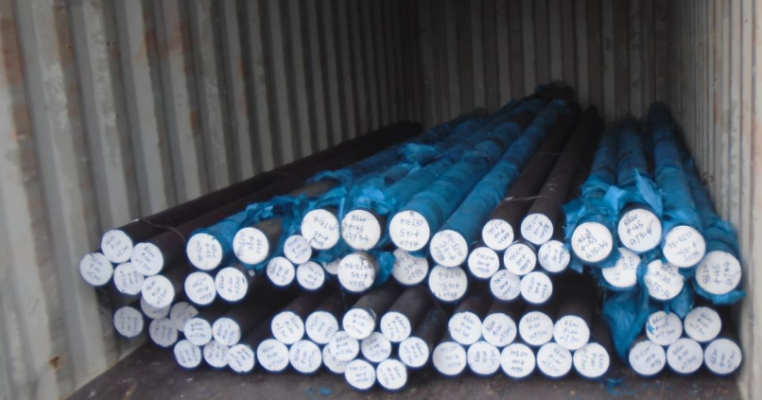
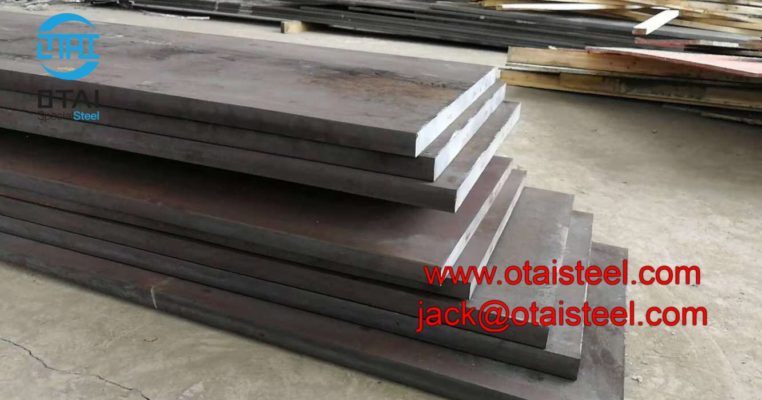
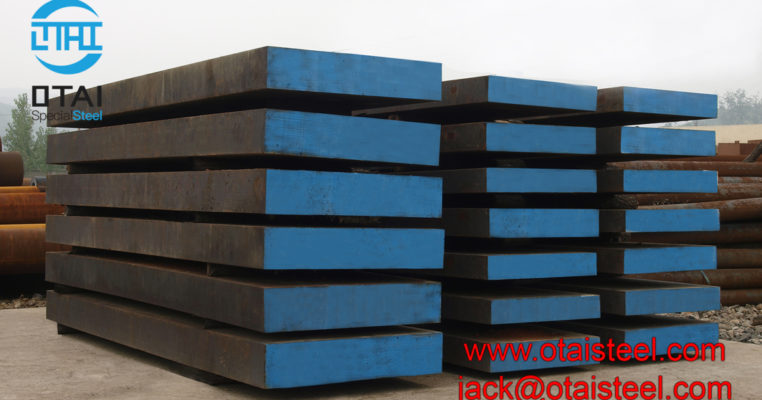
AISI 4130 Qualified Stock from Otai Special Steel AISI 4130 alloy Steel is a high quality Quenched and Tempered Alloy Structural steel, It belong to the high quality low carbon, Oil Quenched & Tempered Hardenss is 28-34 HRc. AISI 4130 steel Annealing delivery hardenss less than 250HB . OTai have many stock with round bar and original sheet plate , the price are competitive all over the year .

AISI 4130 Qualified Stock from Otai Special Steel / Otai Special Steel . AISI 4130 steel is widely used for a variety of applications in the oil and gas sector. Typical applications such as valve bodies, pumps and fittings, Shaft, spindle, and the high load of wheel, bolts, double-headed bolts, gears, etc .
AISI 4130 Qualified Stock from Otai Special Steel / Otai Special Steel . AISI 4130 alloy steel round bar and flat sections can be cut to your required sizes. 4130 alloy steel ground bar can also be supplied, providing a high quality tool steel precision ground tool steel bar to your required tolerances. AISI 4130 steel is also available as Ground Flat Stock / Gauge Plate, in standard and nonstandard sizes .
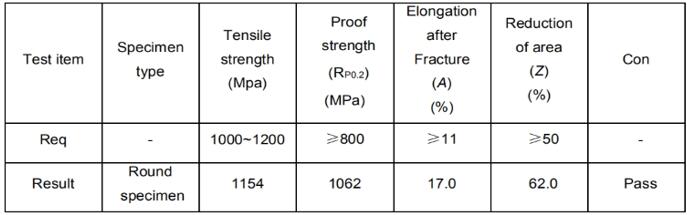
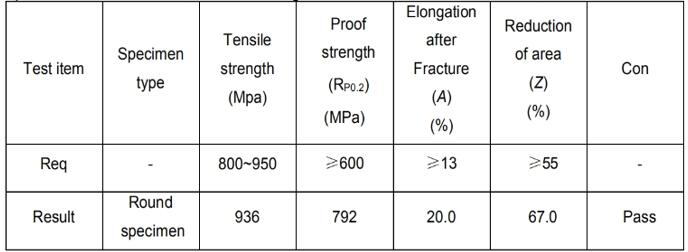
My cutomer from U.S.A need a very big round bar forged to make a rotor , The alloy is 4130 and heat treated to Yield strength of 1120 MPa , Ultimate strength of 1260 MPa , minimum elongation of 6% ,
Thickness = 475 mm (thickness direction is same as blank thickness direction shown in above figure)
Length = 280 mm
Width = 280 mm
For this samples , we have 9 pcs Dia.2110*L580MM Forged round bar orders , and they have used on the fittings of Oakland Machine Works for more than one year , and my customer was very satisfied with the best quality production , and we also happy that we could provide this very complex fitting to them . The next story may with you , waiting for your new inquiry !

Ms Monica Yu
Mobile/WhatsApp: 0086-13711903397
Tel: 0086-769-23190193
Fax: 0086-769-88705839
Email: Monica@otaisteel.com