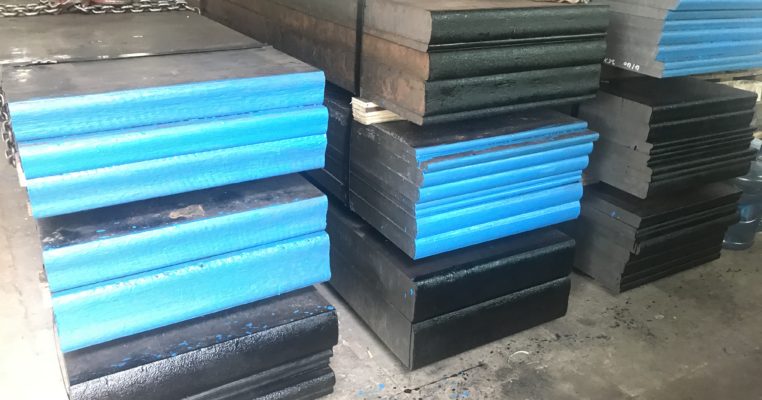
How many tons of 4140 steel plates for sale in our stock?
Otai exports various tool steel and alloy to more than 30 countries from Europe and America, Middle East, and Asia. Our steel materials meet DIN / ASTM / EN / JIS etc different international standards. Otai’s 4140 steel plates for sale: we keep a daily inventory of 1000 tons which is hard for competitors.
4140 alloy steel, the steel has good workability, machining deformation of small, anti-fatigue performance is quite good.
On the hardenability of steel, 4140 heat treatment has good strength and good comprehensive mechanical properties, good manufacturability, high yield. The highest temperature is 427 degrees Celsius. 4140 strength, high hardenability, and good toughness, quenching deformation of small, high temperature creep rupture strength, and high. It is used for manufacturing forgings with higher strength and larger tempering cross-section than 35CrMo steel, such as big gear for locomotive traction, supercharger drive gear, rear axle, connecting rod and spring clamp with great load, also can be used for drilling pipe joint and fishing tool of oil deep well below 2000m, and can be used for bending machine mold, etc.
Customer’s story
We would like to share a real case of our customer with you. Elisa from Poland sent us an inquiry for 4140 alloy steel plates. As time is tight, he needs to receive the goods within 45 days. That’s no problem for us because we keep a daily inventory of 1000 tons. After the customer placed his order, we have prepared his 4140 alloy steel plates to ready the next day. We also assisted the customer to find the fastest delivery, and the goods were delivered to the customer in 45 days.
Otai does not act as a material handler. We possess proprietary technology and continuously iterates. We undertake every order to end and solve customer’s problems without any hesitation on responsibility. When customized special steel is hard to get, Otai settles satisfactorily completely.